In the heart of the Gulf, Saudi Arabia is witnessing a major shift in how people handle their finances, as digital money transfer applications have increasingly replaced traditional cash transactions in 2025. From bustling city malls in Riyadh to small family-run shops in Jeddah, residents are choosing the speed, convenience, and security of digital platforms over physical currency.
This growing preference is largely attributed to the Kingdom’s ambitious Vision 2030 agenda, which prioritises financial technology as a core pillar of economic diversification. With support from both the Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) and the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology, fintech adoption has surged across the population, fuelled by aggressive digitisation policies, investments in infrastructure, and widespread smartphone penetration.
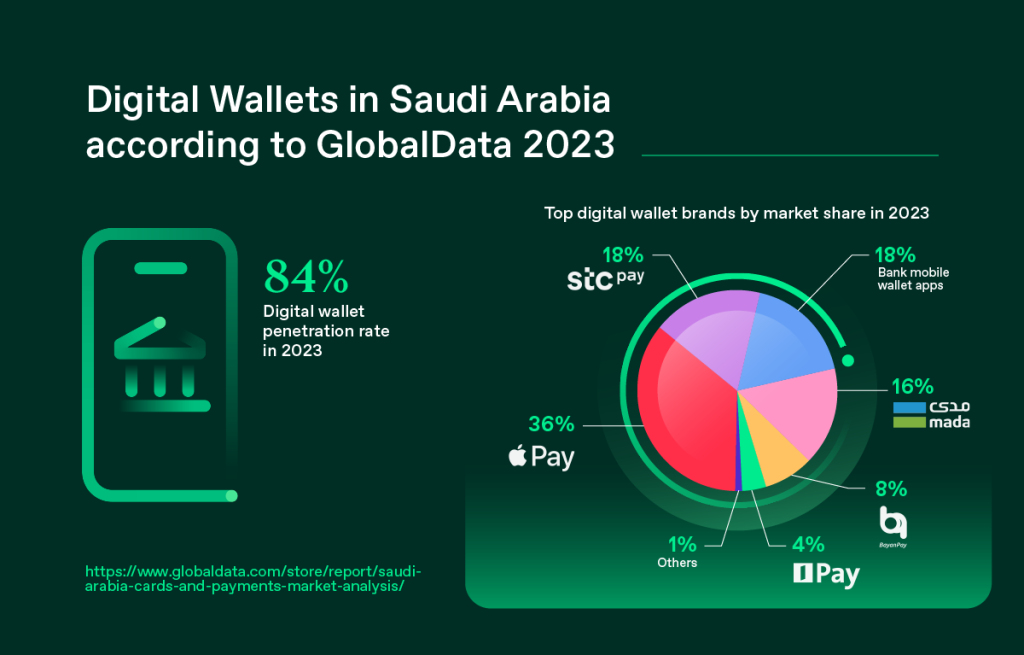
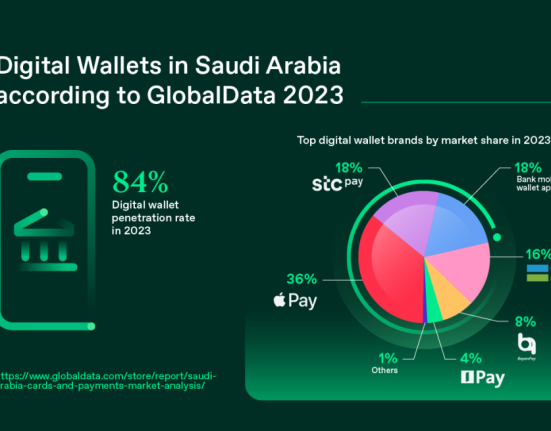
The financial analysts note that cash transactions have steadily declined in Saudi Arabia over the past three years, with 2025 marking a significant tipping point. Citizens and residents alike now rely heavily on apps such as STC Pay, Apple Pay, mada Pay, and other local fintech platforms to carry out day-to-day transactions—from paying for groceries and utility bills to transferring funds across borders within seconds.
One key driver of this trend is convenience. Digital apps have streamlined the payment experience, allowing users to send, receive, and manage money without the need for queues, paper receipts, or ATM visits. Many platforms also offer features such as expense tracking, bill reminders, QR-code payments, and real-time transaction alerts—all of which contribute to a more transparent and user-friendly financial experience.
Security concerns, once a major barrier to digital adoption, have been largely addressed through advanced encryption, biometric verification, and real-time fraud monitoring systems. Today, many users say they feel safer using mobile apps than carrying physical cash.
The COVID-19 pandemic also played a critical role in accelerating the shift toward cashless payments, as public health concerns made physical money less attractive. That momentum has only grown stronger, with digital payment habits becoming deeply embedded in everyday life.
Merchants, too, have embraced the change. From taxis to coffee shops, businesses of all sizes now accept mobile payments, encouraged by low transaction fees, faster settlements, and integration with inventory and accounting tools. Government services, including Zakat, passport fees, and traffic fines, are now payable almost exclusively through electronic channels.
SAMA’s continued regulation and supervision of fintech services have helped foster trust in the digital economy. The Central Bank has also licensed dozens of new players in the space, creating a competitive environment that pushes innovation and improves user experience.
As of Q3 2025, data from the Saudi Central Bank shows that over 80% of all retail transactions in the Kingdom are now conducted electronically—a figure that is expected to rise even further in the coming years.
In a society that once relied heavily on physical currency, Saudi Arabia’s rapid transition to a digitally-driven payment culture is being hailed as a model for the wider Middle East region. The Kingdom’s fintech revolution is not just changing how people pay; it’s redefining the very fabric of financial interaction.